In the era of big data with high-performing computing power, my research interests are focused on developing machine learning algorithms that could have potential big impact on real-world problems. Those problems include but are not limited to: Optimization, Protein Docking, Protein Design, etc.
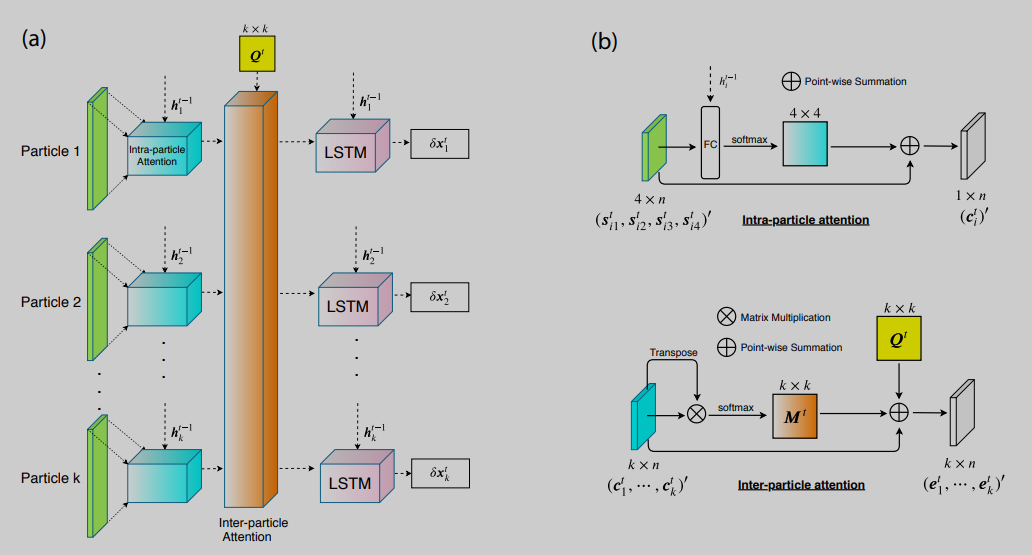
Learning-based Optimization
Optimization provides a mathematical foundation for solving quantitative problems in many fields,
along with numerical challenges. The no free lunch theorem indicates the non-existence of a universally best optimization algorithm for all objectives. To manually design an effective optimization
algorithm for a given problem, many efforts have been spent on tuning and validating pipelines,
architectures, and hyperparameters. To overcome the laborious manual design, an emerging approach of meta-learning (learning to learn) takes advantage of the knowledge learned from related tasks. In meta-learning, the goal is to learn
a meta-learner that could solve a set of problems, where each sample in the training or test set is a particular problem.
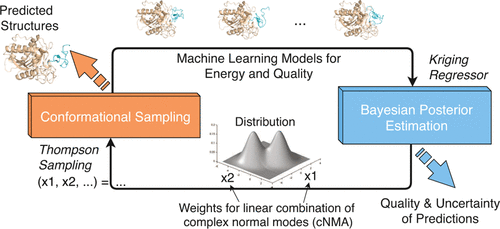
Bayesian Active Learning for Protein Docking
Ab initio protein docking represents a major challenge for optimizing a noisy and costly “black box”-like function in a high-dimensional space. Despite progress in this field, there is a lack of rigorous uncertainty quantification (UQ). To fill the gap, we introduce a novel algorithm, Bayesian active learning (BAL), for optimization and UQ of such black-box functions with applications to flexible protein docking. BAL directly models the posterior distribution of the global optimum (i.e., native structures) with active sampling and posterior estimation iteratively feeding each other. Furthermore, it uses complex normal modes to span a homogeneous, Euclidean conformation space suitable for high-dimensional optimization and constructs funnel-like energy models for quality estimation of encounter complexes.
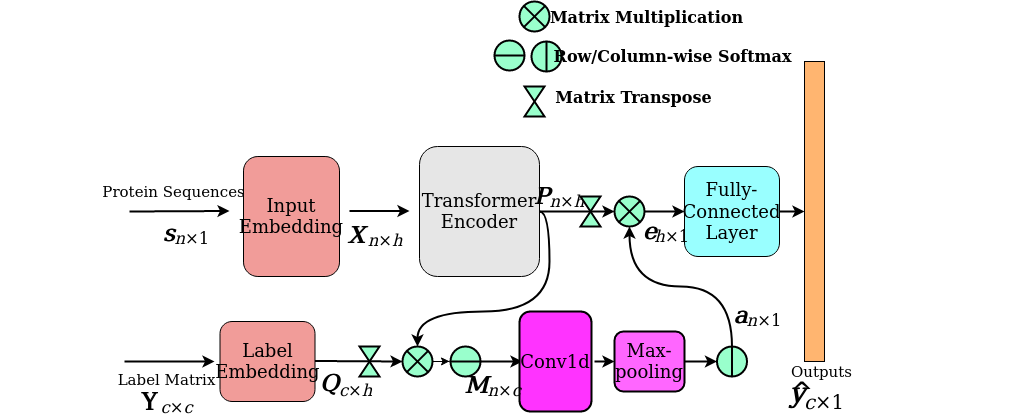
Joint Embedding Learning between Protein Sequneces and their Properties
Joint embedding learning has a large number of applications in texts and images. In this direction, we developed novel joint embedding learning frameworks for protien sequences (1D) and their properties (e.g. structures (3D), fucntions (graph)). We demonstrates the advantages of joint embedding learning based on several tasks including protein function annotation and protein design.